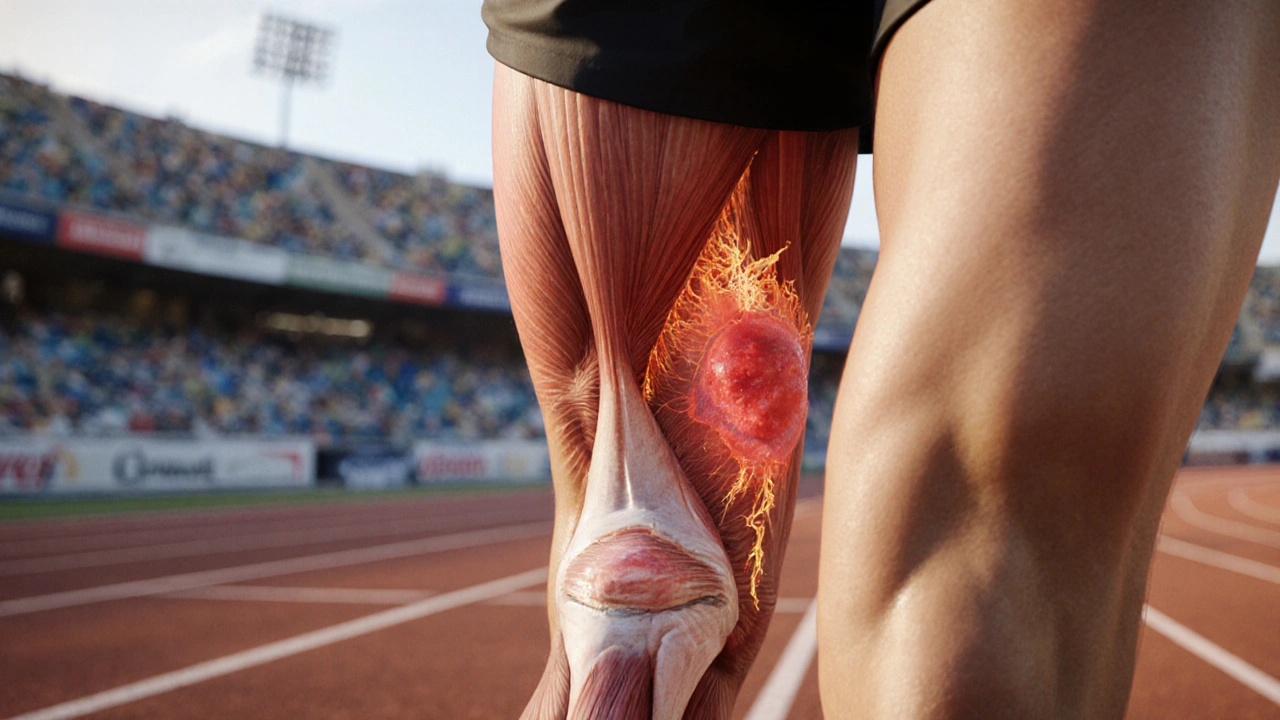
Acute skeletal muscle injuries happen when a muscle fiber is suddenly stretched beyond its limit, causing tears or strains. These injuries are common in sports, manual labour, and everyday mishaps. Within the first few hours, the body launches an inflammatory response, swelling and pain signal that something’s wrong. Managing that early phase effectively can speed up recovery and keep you from missing weeks of activity.
What Actually Happens Inside a Muscle?
The healing timeline can be split into three phases: (1) Inflammation, where blood rushes in to clear debris; (2) a proliferative stage, during which new muscle fibres start to form; and (3) remodeling, where the tissue strengthens. Each stage has its own therapeutic needs. Pain and swelling dominate the first 24‑48hours, while later you’ll focus on restoring strength and flexibility.
Why Medications Are a Core Part of Recovery
Drugs aren’t a magic fix, but they tackle the two biggest roadblocks: pain that limits movement and inflammation that can prolong stiffness. By reducing these, you can start gentle motion sooner, which research shows improves scar alignment and prevents chronic tightness. The right medication, taken at the right time, works hand‑in‑hand with rest, ice, compression, and physiotherapy.
Top Medication Classes and How They Work
Below is a quick rundown of the most common drug groups used for acute muscle injury treatment. Each entry includes typical dosing, onset of action, and safety notes.
- Non‑steroidal anti‑inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen block cyclo‑oxygenase enzymes, lowering prostaglandin production. Onset: 30‑60min. Typical dose: ibuprofen 400‑600mg every 6‑8h (max 2400mg/day). Pros: fast pain relief, reduces swelling. Cons: stomach irritation, kidney strain, may blunt early inflammation needed for tissue repair if overused.
- Acetaminophen works mainly in the central nervous system to raise the pain threshold. Onset: 45‑60min. Typical dose: 500‑1000mg every 4‑6h (max 3000mg/day). Pros: gentle on stomach, safe for most adults. Cons: no anti‑inflammatory effect; high doses risk liver injury.
- Muscle relaxants like cyclobenzaprine act on the brainstem to dampen muscle spindle reflexes. Onset: 1‑2h. Typical dose: 5‑10mg at bedtime. Pros: helpful for spasms that lock a muscle in a painful position. Cons: drowsiness, dry mouth, not for prolonged use.
- Opioids (e.g., tramadol, oxycodone) bind to opioid receptors, providing strong analgesia. Use only for severe pain that doesn’t respond to NSAIDs/acetaminophen. Typical dose varies; start low. Pros: powerful pain control. Cons: dependence, constipation, sedation-reserve for short courses.
- Corticosteroids (e.g., prednisone) suppress the immune cascade more broadly than NSAIDs. Short tapers (5‑10days) can be considered for massive swelling that threatens neurovascular structures. Pros: rapid anti‑inflammatory effect. Cons: blood‑sugar spikes, mood changes, impaired collagen synthesis if used long‑term.
- Topical analgesics (diclofenac gel, menthol‑capsaicin creams) deliver drug locally with minimal systemic exposure. Onset: 15‑30min. Apply 3‑4times daily. Pros: good adjunct for surface pain, low systemic risk. Cons: may cause skin irritation.
Quick Comparison of Medication Options
| Class | Mechanism | Typical Onset | Common Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| NSAIDs | COX inhibition → ↓ prostaglandins | 30‑60min | GI upset, kidney strain |
| Acetaminophen | d>Central COX inhibition → ↑ pain threshold45‑60min | Liver toxicity at high doses | |
| Muscle relaxants | Brainstem inhibition of motor neurons | 1‑2h | Drowsiness, dry mouth |
| Opioids | Opioid receptor agonism | 15‑30min | Constipation, dependence |
| Corticosteroids | Broad immune suppression | Hours to days | Blood‑sugar rise, mood swings |
| Topical analgesics | Local COX inhibition / counterirritant | 15‑30min | Skin redness, itching |
How to Pick the Right Drug for Your Injury
Think of medication choice as a decision tree:
- Assess pain intensity. Mild‑to‑moderate pain? Start with NSAIDs or acetaminophen.
- If swelling is pronounced, NSAIDs give the added anti‑inflammatory boost.
- When muscle spasm limits range of motion, add a single dose of a muscle relaxant.
- Severe pain that blocks sleep may warrant a short‑term opioid, but only under medical supervision.
- Consider health background: ulcer disease → avoid NSAIDs; liver disease → limit acetaminophen; diabetes → cautious with steroids.
Always discuss dosing with a clinician, especially if you’re taking other medicines that could interact (e.g., blood thinners and NSAIDs).

Medications Work Best With Non‑Drug Care
Even the best drug won’t fix a torn fibre alone. Combine medicine with the classic RICE protocol (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) during the first 48hours, then transition to gentle stretching under the guidance of physiotherapy. Early, pain‑free movement helps align collagen fibers correctly, reducing the chance of scar tissue that feels stiff months later.
Practical Checklist Before You Take a Pill
- Do I have any allergies or chronic conditions that limit certain drugs?
- What is my current pain level on a 0‑10 scale?
- Is swelling impeding movement or blood flow?
- Am I already using other OTC meds or prescriptions that could interact?
- Do I need a prescription strength (e.g., opioid) or will an OTC dose suffice?
- When should I seek medical attention? (e.g., inability to bear weight, numbness, severe bruising)
Answering these questions keeps you safe and helps the clinician tailor a plan quickly.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use NSAIDs for a muscle tear that’s more than a few days old?
Yes, but limit use to the first 5‑7days. After that, the anti‑inflammatory effect may interfere with the remodeling phase. Switching to acetaminophen or topical agents helps control lingering pain without dampening healing.
Are muscle relaxants safe for athletes?
They’re safe for short bursts (usually one‑night dose) to break a painful spasm. Because they cause drowsiness, avoid taking them before training or competition.
When is a corticosteroid injection justified?
Only when swelling threatens neurovascular structures or when the injury is part of a chronic inflammatory condition (e.g., myositis). A single low‑dose steroid can reduce swelling dramatically, but it must be followed by a gradual rehab program.
Do topical NSAIDs work as well as oral ones?
For superficial pain (e.g., bruised quadriceps) they’re quite effective and avoid systemic side effects. For deeper injuries, oral NSAIDs usually achieve higher tissue concentrations.
What red‑flag symptoms mean I need urgent care?
Sudden, severe pain with loss of sensation, a rapidly expanding bruise, inability to move the limb at all, or signs of infection (fever, warmth, pus). These warrant immediate medical evaluation.
Medication isn’t a stand‑alone cure, but when you match the right drug to the right stage of an acute skeletal muscle injury, you shave off days of downtime and set the stage for a stronger return. Talk to a healthcare professional, follow the dosage guidelines, and pair drugs with gentle movement for the best results.



SHASHIKANT YADAV
October 12, 2025 AT 15:48Nice summary! 👍
Ryan Pitt
October 13, 2025 AT 19:36Glad you found it useful-if you’re dealing with a strain, start with a low dose NSAID and ice, then ease into gentle stretching. Keep it simple and listen to your body.
Jami Johnson
October 14, 2025 AT 23:40When a muscle tears, it is as if Nature herself has taken a sudden, jagged breath.
The inflammatory fire that follows is not a villain but a messenger, signaling the need for repair.
To blunt that fire with medicine is to negotiate with the body's own wisdom.
NSAIDs arrive like a courteous diplomat, soothing pain while risking the subtle art of tissue remodeling.
Acetaminophen, on the other hand, is the quiet monk, raising the threshold of suffering without meddling in the inflammatory council.
Muscle relaxants are the gentle lullaby that quiets the hyper‑active spindles, granting the injured fibres a moment of peace.
Opioids explode onto the scene as fierce warriors, offering swift relief but demanding respect to avoid the shadows of dependence.
Corticosteroids, the fire‑bringers, can quell dangerous swelling in a flash, yet their flame may scorch collagen if left unchecked.
Topical agents whisper across the skin, delivering modest comfort while sparing the heart of the system.
The true hero, however, is movement-controlled, painless motion that aligns scar tissue like a master sculptor.
RICE in the early hours is the scaffold, but without the gentle stretch, the structure may crumble under future strain.
Choosing the right drug is akin to selecting the proper brush for a painting; each stroke matters.
Remember to weigh personal history-ulcers, liver health, and diabetes are the silent judges of our pharmacologic decisions.
A clinician’s guidance acts as the compass, steering us through the tempest of side‑effects and interactions.
In the end, the harmonious blend of medication, rest, and progressive rehab fashions a return not merely to function, but to a stronger, wiser self.
Kasey Krug
October 16, 2025 AT 03:43The article is thorough, but it overstates the benefit of NSAIDs; excessive use can indeed hinder remodeling. A more balanced view would caution against routine high‑dose regimens.
jake cole
October 17, 2025 AT 07:46What a load of fluff. Anyone actually believes popping pills fixes a torn muscle? Get real and stop glorifying pharmaceuticals.
Natalie Goldswain
October 18, 2025 AT 11:50lol, i get ur point but in some cultures we rely on natural remedies like turmeric paste, it works decent for mild pain.
khajohnsak Mankit
October 19, 2025 AT 15:53The cascade of biochemical whispers after injury is a kaleidoscope of opportunity; each medication paints a hue on the canvas of recovery, turning crimson pain into a spectrum of healing.
Jayant Paliwal
October 20, 2025 AT 19:56Indeed, the pharmacologic palette is vast, and while your poetic metaphor captivates the imagination, let us not forget the practicalities-dosage timing, metabolic pathways, patient compliance, and the ever‑present risk of adverse effects, all of which demand rigorous attention, especially in the acute phase; otherwise, even the most eloquent description fails to translate into tangible benefit.
Kamal ALGhafri
October 22, 2025 AT 00:00From a mechanistic standpoint, inhibiting COX enzymes is the most direct method to reduce prostaglandin-mediated edema; any deviation from this principle must be justified by solid clinical evidence.
Gulam Ahmed Khan
October 23, 2025 AT 04:03Absolutely! 😊 Stick to the basics, and you’ll see faster recovery-just remember to combine it with the proper rehab exercises.
John and Maria Cristina Varano
October 24, 2025 AT 08:06i dont care about foreign med advice its us medical stuff that works better dont listen to westerner.
Melissa Trebouhansingh
October 25, 2025 AT 12:10While one might be inclined to dismiss the merits of evidence‑based guidelines in favor of parochial sentiment, such a stance overlooks the universality of pharmacological principles that transcend cultural borders; indeed, the rigorous trials conducted across continents serve as the bedrock of our collective medical knowledge.
Brian Rice
October 26, 2025 AT 15:13It is incumbent upon the discerning reader to recognize the pernicious allure of self‑medication, a practice that, unchecked, erodes both personal responsibility and the sanctity of professional medical counsel.
Stan Oud
October 27, 2025 AT 19:16Sure, but if the system is slow to respond, patients will inevitably turn to alternatives; dismissing that reality does not solve the underlying issue.