More than 6 million Americans live with Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) every year. For many, the constant worry isn’t just stress-it’s a physical burden: racing heart, tight muscles, sleepless nights, and a mind that won’t shut off. The good news? We have effective ways to treat it. The bad news? Not all treatments are created equal. Some offer quick relief but come with hidden costs. Others take time but change how you live with anxiety for good.
What Exactly Is Generalized Anxiety Disorder?
GAD isn’t just being nervous before a presentation. It’s worrying about everything-your job, your health, your kids, even things you can’t control-and doing it most days for six months or longer. The DSM-5, the official guide doctors use to diagnose mental health conditions, says GAD involves at least three physical or mental symptoms like restlessness, fatigue, trouble concentrating, irritability, muscle tension, or sleep problems. It’s not a phase. It’s not weakness. It’s a real, measurable condition that changes how your brain processes threat.
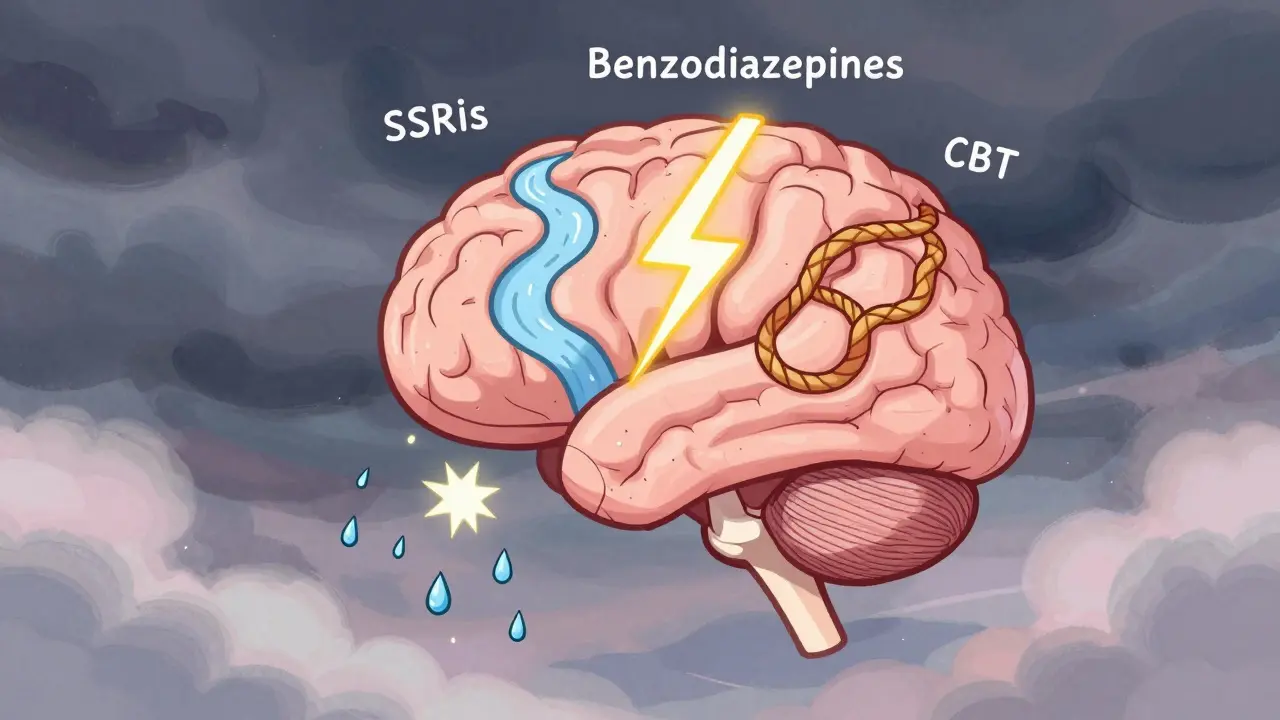
SSRIs: The First-Line Medication That Takes Time
When doctors start treating GAD with medication today, they almost always reach for an SSRI first. That stands for selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor. Common ones include escitalopram (Lexapro), sertraline (Zoloft), and paroxetine (Paxil). These drugs don’t calm you down right away. In fact, you might feel worse before you feel better.
Why? Because SSRIs work by slowly increasing serotonin levels in your brain. That takes 2 to 6 weeks to make a difference. Some people notice small improvements in sleep or energy after the first week, but full relief usually comes around week 4 or 5. The upside? Once it works, it keeps working. Studies show 50-60% of people respond well to SSRIs. And unlike other meds, they don’t cause dependence.
Side effects are real but manageable. Nausea, headaches, and sexual dysfunction affect nearly half of users, especially early on. Most people get used to them. Doctors usually start with a low dose-like 12.5 mg of escitalopram-and increase it slowly to reduce side effects. If one SSRI doesn’t work, another might. It’s trial and error, but it’s safe for long-term use.
Benzodiazepines: Fast Relief, High Risk
If you’ve ever taken Xanax or Ativan for a panic attack, you’ve used a benzodiazepine. These drugs-like alprazolam, lorazepam, and diazepam-work fast. Really fast. Within 30 to 60 minutes, they calm your nervous system by boosting GABA, the brain’s natural calming chemical. For someone in crisis, that’s life-changing.
But here’s the catch: your brain adapts. After just a few weeks, you need more to get the same effect. That’s tolerance. After 3 to 6 months, nearly half of users need higher doses just to feel stable. Stopping suddenly can trigger seizures, rebound anxiety, or insomnia worse than before. Withdrawal can last months.
That’s why guidelines from the American Psychiatric Association, NICE, and the VA/DoD all say: don’t use benzodiazepines as a first-line treatment. They’re not wrong-they’re just not meant for daily, long-term use. They’re for emergencies: a flight you can’t cancel, a medical procedure, or a panic attack that won’t quit. Even then, most doctors now limit prescriptions to 2-4 weeks and require regular check-ins.
On Drugs.com, alprazolam has a 7.4/10 rating. But 72% of users report side effects: drowsiness, dizziness, memory gaps. One Reddit user wrote, “I felt like a zombie for six months. When I quit, my anxiety came back harder.” That’s not rare.

Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Training Your Brain
CBT is the only treatment here that doesn’t change your chemistry-it changes your thinking. It’s not talking about your childhood. It’s learning to catch distorted thoughts like “I’m going to fail,” “Everyone thinks I’m weird,” or “This headache means I have a tumor.” Then you test them. Is that thought based on facts? Or fear?
A standard CBT program for GAD lasts 12 to 20 weekly sessions. You learn skills: how to challenge worry, how to sit with discomfort without reacting, how to face situations you’ve been avoiding. You get homework-yes, real homework. Writing down worries, doing exposure exercises, tracking patterns. About 65-75% of people who do the work see big improvements.
Here’s the kicker: CBT works as well as medication at the end of treatment. But one year later? CBT wins. Studies show only 25% of people who did CBT relapse, compared to 45% who stopped taking SSRIs. Why? Because you didn’t just get relief-you learned how to handle anxiety yourself. It’s like learning to swim instead of always needing a life jacket.
The biggest barrier? Access. A single CBT session costs $100-$150 out of pocket. Insurance often covers it, but finding a certified therapist can take months. That’s why apps like Woebot and SilverCloud are filling the gap. They’re not perfect, but they’re better than nothing. A 2021 study in JAMA Internal Medicine showed digital CBT reduced anxiety by 30-40% over 12 weeks.
Which Treatment Should You Choose?
There’s no one-size-fits-all. But here’s how most people end up choosing:
- If you’re in crisis-can’t sleep, can’t leave the house, panic attacks daily-start with a short course of a benzodiazepine (under strict supervision) while you begin CBT or start an SSRI.
- If you’re dealing with long-term worry and have depression too (60% of GAD patients do), SSRIs are your best bet. They treat both.
- If you want lasting change, don’t just medicate. Do CBT. Even if it’s hard. Even if it’s expensive. The skills stick.
Many people combine treatments. A 2022 JAMA Network Open study found that patients on both an SSRI and CBT had a 65% remission rate-much higher than either alone. That’s the new standard: medication to get you stable, therapy to keep you well.

What’s Changing Right Now?
The field is shifting fast. In 2023, the FDA approved zuranolone (Zurzuvae), a new drug that works like benzodiazepines but with far less risk of dependence. Early trials showed only 5% withdrawal symptoms, compared to 25% with traditional benzos. It’s not a magic bullet, but it’s a sign that safer options are coming.
Genetic testing is also entering the game. Companies like GeneSight analyze your DNA to predict which SSRIs your body will respond to best. In a 2023 study, patients who got tested had 28% better outcomes. That’s not mainstream yet-but it’s coming.
And CBT? It’s going digital. More than 70% of therapists now offer telehealth. Apps are getting smarter. Insurance is slowly catching up. The 2022 Mental Health Access Improvement Act expanded Medicare coverage for counselors, making CBT more affordable for older adults.
Benzodiazepines? Their use is declining. Prescriptions dropped 18% since 2015. Regulators now require boxed warnings about addiction risk. Doctors are more cautious. That’s good. But it’s also creating a gap-some people who need short-term help can’t get it because providers are afraid to prescribe.
What to Do If You’re Struggling
If you think you have GAD, start with your primary care doctor. They can screen you and refer you to a mental health specialist. Don’t self-medicate. Don’t delay. The longer anxiety goes untreated, the harder it is to reverse.
If you’re already on medication:
- Don’t quit SSRIs cold turkey. Taper slowly under medical supervision.
- If you’re on benzodiazepines long-term, talk to your doctor about a taper plan. The Ashton Manual is the gold standard for safe withdrawal.
- Ask about CBT. Even if you’re on meds, therapy adds a layer of protection against relapse.
Cost is a real barrier. But free or low-cost CBT programs exist through universities, community clinics, and nonprofits. Some apps offer sliding scale fees. And many insurance plans now cover teletherapy.
Anxiety doesn’t have to be your default setting. You don’t have to choose between feeling numb or feeling overwhelmed. There’s a middle path-safe, effective, and sustainable. You just need to know where to look.
Can SSRIs make anxiety worse at first?
Yes. In the first 1-2 weeks of starting an SSRI, some people feel more anxious, restless, or even have increased panic attacks. This is temporary and happens because serotonin levels are adjusting. It’s not a sign the drug isn’t working-it’s part of the process. Most people see improvement after 2-4 weeks. If symptoms are severe or don’t improve after 4 weeks, talk to your doctor about adjusting the dose or switching meds.
Are benzodiazepines ever safe for long-term use?
Most guidelines say no. Long-term use increases the risk of dependence, cognitive decline, falls in older adults, and withdrawal symptoms that can be worse than the original anxiety. However, a small subset of patients-those who’ve tried everything else and are closely monitored-may benefit from low-dose, long-term use. This is not standard practice and requires frequent check-ins with a specialist. It’s not recommended for anyone under 65 without exhausting other options first.
How do I know if CBT is working for me?
You’ll notice small changes early: you catch yourself worrying and pause before spiraling. You start asking, “Is this thought true?” instead of believing it automatically. After 6-8 sessions, you’ll likely feel more in control during stressful moments. Homework compliance is key-people who do their assignments are 2.3 times more likely to see major improvement. If after 12 sessions you feel no change, ask your therapist to adjust the approach.
What’s the difference between panic disorder and GAD?
Panic disorder involves sudden, intense episodes of fear with physical symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, or dizziness-often mistaken for a heart attack. These attacks come out of nowhere. GAD is more constant: a low-grade, persistent worry about everyday things-money, health, family, work-that lasts for months. People with GAD rarely have full panic attacks, but they’re always on edge. Treatment is similar, but CBT for GAD focuses more on worry reduction, while panic disorder CBT targets fear of bodily sensations.
Can I stop taking SSRIs once I feel better?
Don’t stop abruptly. Even if you feel fine, stopping too soon increases relapse risk. Most doctors recommend staying on SSRIs for at least 6-12 months after symptoms improve. For people with chronic GAD, longer use (2+ years) may be needed. If you want to stop, work with your doctor to taper slowly-over weeks or months. Stopping suddenly can cause dizziness, brain zaps, nausea, or rebound anxiety.
Is therapy better than medication for anxiety?
It depends on your goal. If you need fast relief, medication wins. If you want to avoid lifelong dependence and build lasting skills, therapy wins. Studies show CBT and SSRIs are equally effective at the end of treatment. But one year later, CBT has lower relapse rates. Many experts now recommend combining both: use medication to stabilize, then use therapy to heal. That’s the most effective long-term strategy.

Hilary Miller
January 22, 2026 AT 01:33Margaret Khaemba
January 22, 2026 AT 12:19Malik Ronquillo
January 22, 2026 AT 16:32Brenda King
January 22, 2026 AT 20:51Daphne Mallari - Tolentino
January 23, 2026 AT 15:22Philip House
January 23, 2026 AT 20:06Mike P
January 25, 2026 AT 06:04Jasmine Bryant
January 26, 2026 AT 01:44Liberty C
January 27, 2026 AT 07:10shivani acharya
January 27, 2026 AT 19:37Sarvesh CK
January 29, 2026 AT 14:58Keith Helm
January 29, 2026 AT 21:31Neil Ellis
January 30, 2026 AT 00:37Alec Amiri
January 30, 2026 AT 20:26Lana Kabulova
January 30, 2026 AT 21:23