NSAIDs: What They Are, How They Work, and Which Alternatives Actually Help
When you reach for a pill to calm a headache, sore muscles, or joint pain, you’re probably reaching for a NSAIDs, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that reduce pain, fever, and swelling. Also known as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories, these are among the most widely used medications in the world — from ibuprofen on your kitchen counter to prescription-strength options like mefenamic acid. But not all NSAIDs work the same way, and not everyone can take them safely.
NSAIDs block enzymes that cause inflammation, but that same action can irritate your stomach, raise blood pressure, or strain your kidneys. That’s why people with ulcers, heart disease, or kidney issues often need alternatives. Acetaminophen, a pain reliever that doesn’t reduce inflammation but is gentler on the stomach is a common go-to for post-accident pain or mild arthritis. Then there’s Ponstel, the brand name for mefenamic acid, a specific NSAID often used for menstrual cramps and known for its shorter duration and different side effect profile. While it’s still an NSAID, its use case and risks differ from ibuprofen or naproxen.
What you might not realize is that NSAIDs aren’t always the best first choice. For muscle injuries, combining them with rest and physical therapy often works better than just popping pills. For chronic pain, long-term NSAID use can do more harm than good — especially if you’re also taking blood pressure meds or diuretics like amiloride. And if you’re pregnant, some NSAIDs can affect fetal development, which is why doctors often recommend acetaminophen instead.
The posts below cover real-world scenarios: how NSAIDs stack up against other painkillers, when they’re risky, and what to use when they don’t cut it. You’ll find comparisons between Ponstel and other NSAIDs, how acetaminophen fits into recovery after injury, and why some people need to avoid these drugs entirely. No fluff. Just clear, practical info to help you make smarter choices about your pain relief — without guessing what’s safe or effective.
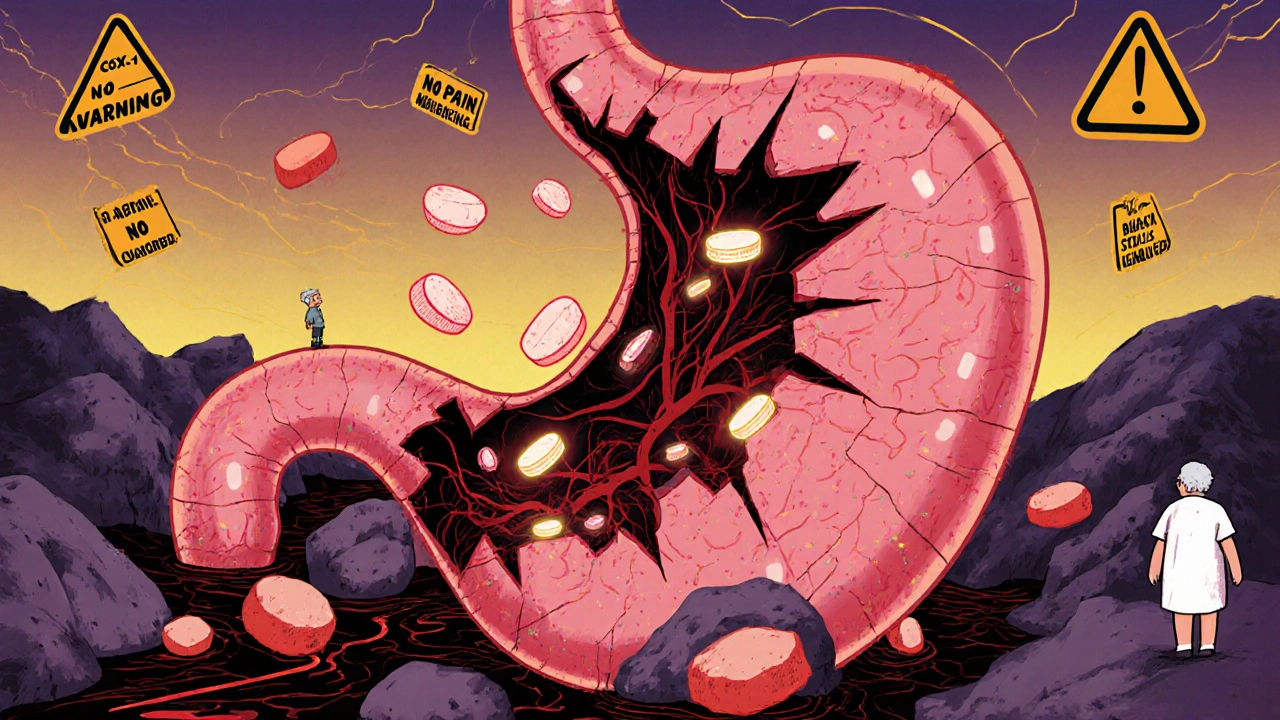
NSAIDs and Peptic Ulcer Disease: Understanding the Risk of Gastrointestinal Bleeding
NSAIDs like ibuprofen and naproxen can cause serious stomach bleeding, especially in older adults or those with risk factors. Learn who’s most at risk, how to protect yourself with PPIs, and safer alternatives for long-term pain relief.
About
Medications